NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide)
Could we extend our years with this Anti-Aging “Longevity Molecule NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide)”?
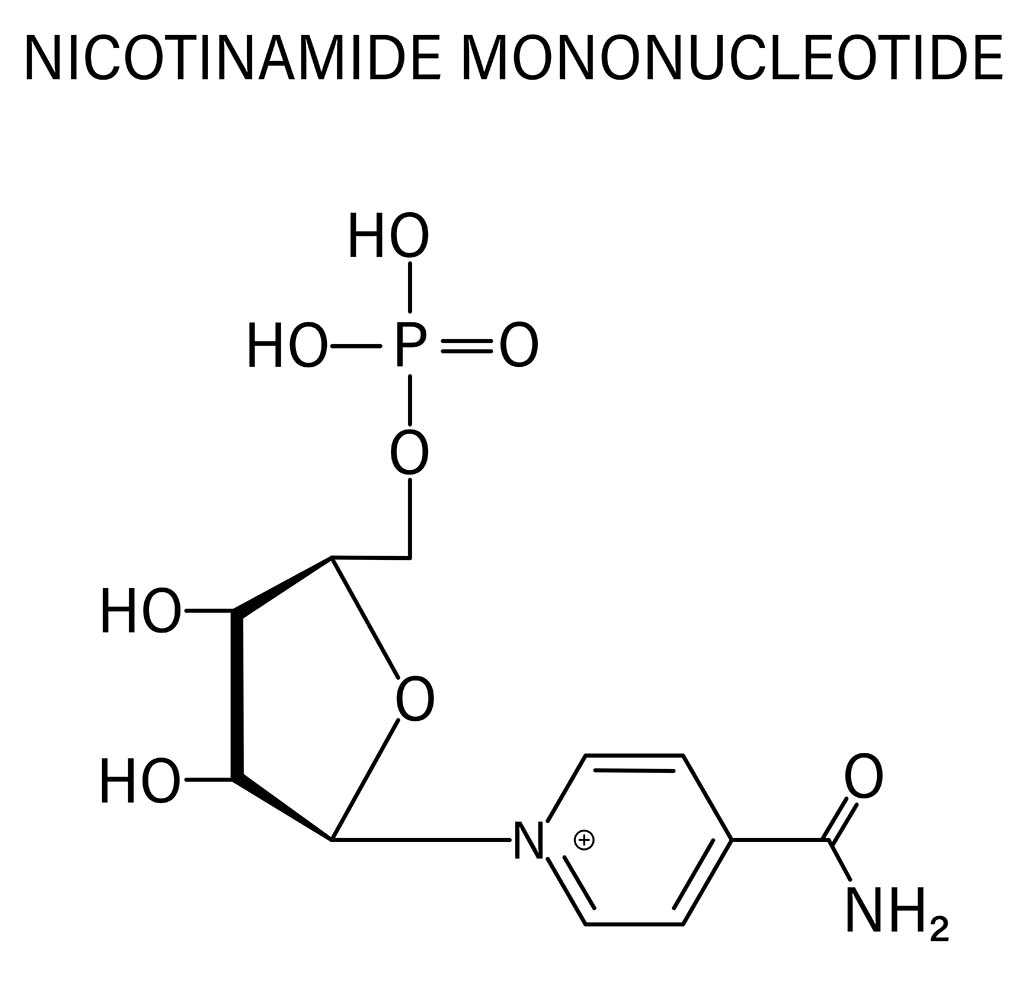
NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide. Like nicotinamide riboside, NMN is a derivative of niacin. Studies show that NMN may improve adult human metabolism so much that it can turn off the genes that accelerate the aging process.
Slow the aging process and restore your metabolism with NMN
Did you know that the World Health Organization (WHO) classified aging as a disease in 2018?
It doesn’t quite make sense since aging is the cause of age-related disease. Aging is a natural evolutionary process of all living things. But what if science could slow down aging or eventually make it obsolete?
Does that mean you’d be able to live forever? Not quite. But it might mean that your longevity could be extended years, or maybe decades beyond today’s norm. And if you do live to a ripe old age, your golden years might be truly golden instead of filled with multiple weekly doctor visits.
The classification of aging as a disease opens up possibilities for new research and novel therapeutics to delay and/or reverse age-related illness. Aging research is discovering that the rate of aging is controlled, to some extent, by biochemical processes and genetic pathways.1
One such discovery is that NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) might improve adult human metabolism so much that it can turn off the genes that accelerate the aging process.
What is NMN?
NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) is a naturally occurring molecule found in all living cells. In humans, it is created by using the B vitamins present in your body.
NMN is a basic structural unit of RNA. Remembering back to high school biology, there are two main types of nucleic acids: 1) DNA provides the code for cellular activity. 2) RNA converts that code into proteins that carry out cellular functions including cell division, differentiation and growth, and cell aging and death. In simple language, NMN helps keep our DNA healthy and reduces the risk of chronic disease and premature death.
You can get NMN naturally from some fruits and veggies such as avocados, broccoli, cabbage, cucumbers, and edamame. But you’d have to eat a lot of these foods to obtain the anti-aging benefits that an NMN supplement can provide.
In addition to being a component of RNA, NMN is a precursor molecule of the essential molecule NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).
What is NAD?
NAD+ is a coenzyme found in all living cells. It’s essential to life because it’s involved in critical cellular functions, including converting food into energy, repairing DNA damage, strengthening the immune system, burning fat, and regulating the body’s circadian clock. It also boosts the activity of sirtuins, a group of seven genes that regulate the aging process.
As we age, NAD naturally declines. We also use more NAD as we get older because our bodies experience more damage from accumulated stress and just sheer living. In fact, scientists describe the slow process of aging as a “cascade of robustness breakdown triggered by a decrease in NAD.” In other words, as NAD+ goes down, cell and tissue age increase. 2-5
How to restore NAD+ balance to counteract functional decline.
You may have heard about (or tried) intermittent fasting and caloric restriction. Studies show this increases NAD+ levels and boost sirtuin activity in mice. But mice aren’t people, and fasting isn’t easy.6
There’s an easier way to increase NAD+ in order to boost cellular energy production and repair, and MUCH MORE!
David Sinclair, a Harvard professor of genetics and renowned anti-aging researcher, is guiding his laboratory team to do cutting-edge research on NMN. He explains that sirtuins, our longevity genes, are turned on by lifestyle activities such as exercise and calorie restriction. Sirtuins can also be activated by increasing NAD.
Harvard Magazine (Sept-Oct 2017) quoted Sinclair as saying that after feeding mice NMN, “We get the same effects as exercise or dieting. The mice are leaner and have more energy. They can run further on a treadmill.”
Numerous studies on laboratory animals have shown that NMN supplementation suppresses age-associated body weight gain, enhances energy metabolism, promotes physical activity, improves insulin sensitivity and plasma lipid profile, improves cognitive function, restores fertility in aging female mice, ameliorates eye function, helps repair kidney damage, improves bone density, expands lifespan, and helps other pathophysiologies. 7-12
REJUV NMN™ ESSENTIAL supports NAD+ production
NAD plays a critical role in many biological processes, including metabolism, inflammation, and stress and damage response. NAD decreases can result in serious physiological decline over time. 13
What can REJUV NMN™ ESSENTIAL with nicotinamide mononucleotide do for you?
- Slow down the aging process by activating sirtuins (the proteins that regulate cellular health, inflammation, and gene repair)
- Promote youthful vitality
- Supports healthy glucose levels 14
- Replenish depleted NAD+ levels 14
- Improve insulin sensitivity in muscle 15
- Increase platelet-derived growth factor b 15
- Enhance energy and metabolism 16
- Boost physical endurance 16
- Enhance aerobic capacity during exercise training 16
- Supports brain function 17
Human clinical studies are underway at numerous laboratories and will undoubtedly demonstrate more verifiable health benefits that NMN supplementation offers.
In the meantime, don’t wait to slow down your biological clock. Start taking REJUV NMN™ ESSENTIAL with nicotinamide mononucleotide now to prevent chronic disease and illness later . . . so your golden years can be truly golden.
Scientific human studies
- The results of the first human clinical study to show that NMN safely increases NAD+ in various organs and improves age-related decline and disease conditions were published in the Endocrine Journal on November 2, 2019. Ten healthy men between the ages of 40 and 60 were given a single oral dose of 100, 250, or 500 mg of NMN. The results found that a single dose of NMN increased NAD levels, supported healthy glucose levels, and was safe and effectively metabolized. 14
- The second human study, published in the journal Science on June 11, 2021, evaluated the effect of NMN supplementation on metabolic function in postmenopausal, overweight women with prediabetes. The 10-week, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial found that NMN increases NAD+ levels. The supplementation also increased muscle insulin sensitivity and platelet-derived growth factor b. Platelet-derived growth factor helps heal wounds, repairs damage to blood vessel walls, and helps blood vessels grow. 15
- A recently published study in the Journal of International Society of Sports Nutrition July 8, 2021, found that NMN supplementation enhances aerobic capacity in amateur runners during training, and boosted energy, metabolism, and endurance. The improvement is likely due to the result of enhanced oxygen utilization of the skeletal muscle. The six-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial separated the participants into four groups: the low dosage group (300 mg/day NMN), the medium dosage group (600 mg/day NMN), the high dosage group (1200 mg/day NMN), and the control group (placebo). Each group consisted of ten male participants and two female participants. Each training session was 40–60 min, and the runners trained 5–6 times each week.
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing was performed at baseline and after the intervention, at 6 weeks, to assess the aerobic capacity of the runners. 16 - When aged laboratory animals were treated with NMN supplementation, the researchers found that it improved endothelial functions — the tissue that forms a single layer of cells lining various organs and cavities of the blood, especially the blood vessels, heart, and lymphatic vessels). It also improved higher brain and cognitive function. 17
Clinical trials are underway to assess the role that NMN might play in preventing age-induced vascular cognitive impairment.17
What’s in Rejuv NMN Essential?
REJUV NMN™ ESSENTIAL is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide. Like nicotinamide riboside, NMN is a derivative of niacin.
When REJUV NMN™ ESSENTIAL is taken along with WeBlume’s RESVER Q™ ANTI-AGING, the resveratrol acts as an accelerator to speed up the pace at which sirtuins work.
Is NMN safe?
Yes. NMN is very safe. The Sinclair Lab at Harvard Medical School demonstrated that one year of oral administration of NMN nicotinamide mononucleotide to laboratory mice did not have any toxic effects. The human studies were also carried out without any negative reports.
References
- Bitto A, Wang AM, Bennett CF, Kaeberlein M. Biochemical Genetic Pathways that Modulate Aging in Multiple Species. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015 Nov 2;5(11):a025114. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a025114. PMID: 26525455; PMCID: PMC4632857.
- López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013 Jun 6;153(6):1194-217. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039. PMID: 23746838; PMCID: PMC3836174.
- Schultz MB, Sinclair DA. Why NAD(+) Declines during Aging: It’s Destroyed. Cell Metab. 2016 Jun 14;23(6):965-966. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.022. PMID: 27304496; PMCID: PMC5088772.
- Imai SI. The NAD World 2.0: the importance of the inter-tissue communication mediated by NAMPT/NAD+/SIRT1 in mammalian aging and longevity control. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2016;2:16018. Published 2016 Aug 18. doi:10.1038/npjsba.2016.18
- Johnson S, Imai SI. NAD + biosynthesis, aging, and disease. F1000Res. 2018 Feb 1;7:132. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.12120.1. PMID: 29744033; PMCID: PMC5795269.
- Madeo F, Carmona-Gutierrez D, Hofer SJ, Kroemer G. Caloric Restriction Mimetics against Age-Associated Disease: Targets, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Potential. Cell Metab. 2019 Mar 5;29(3):592-610. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.01.018. PMID: 30840912.
- Mills KF, Yoshida S, Stein LR, Grozio A, Kubota S, Sasaki Y, Redpath P, Migaud ME, Apte RS, Uchida K, Yoshino J, Imai SI. Long-Term Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Mitigates Age-Associated Physiological Decline in Mice. Cell Metab. 2016 Dec 13;24(6):795-806. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.013. Epub 2016 Oct 27. PMID: 28068222; PMCID: PMC5668137.
- Bertoldo MJ, Listijono DR, Ho WJ, Riepsamen AH, Goss DM, Richani D, Jin XL, Mahbub S, Campbell JM, Habibalahi A, Loh WN, Youngson NA, Maniam J, Wong ASA, Selesniemi K, Bustamante S, Li C, Zhao Y, Marinova MB, Kim LJ, Lau L, Wu RM, Mikolaizak AS, Araki T, Le Couteur DG, Turner N, Morris MJ, Walters KA, Goldys E, O’Neill C, Gilchrist RB, Sinclair DA, Homer HA, Wu LE. NAD+ Repletion Rescues Female Fertility during Reproductive Aging. Cell Rep. 2020 Feb 11;30(6):1670-1681.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.058. PMID: 32049001; PMCID: PMC7063679.
- Kiss T, Nyúl-Tóth Á, Balasubramanian P, Tarantini S, Ahire C, Yabluchanskiy A, Csipo T, Farkas E, Wren JD, Garman L, Csiszar A, Ungvari Z. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation promotes neurovascular rejuvenation in aged mice: transcriptional footprint of SIRT1 activation, mitochondrial protection, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects. Geroscience. 2020 Apr;42(2):527-546. doi: 10.1007/s11357-020-00165-5. Epub 2020 Feb 13. PMID: 32056076; PMCID: PMC7206476.
- Tarantini S, Valcarcel-Ares MN, Toth P, Yabluchanskiy A, Tucsek Z, Kiss T, Hertelendy P, Kinter M, Ballabh P, Süle Z, Farkas E, Baur JA, Sinclair DA, Csiszar A, Ungvari Z. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation rescues cerebromicrovascular endothelial function and neurovascular coupling responses and improves cognitive function in aged mice. Redox Biol. 2019 Jun;24:101192. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101192. Epub 2019 Apr 10. PMID: 31015147; PMCID: PMC6477631.
- Jia Y, Kang X, Tan L, Ren Y, Qu L, Tang J, Liu G, Wang S, Xiong Z, Yang L. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Attenuates Renal Interstitial Fibrosis After AKI by Suppressing Tubular DNA Damage and Senescence. Front Physiol. 2021 Mar 23;12:649547. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.649547. PMID: 33833691; PMCID: PMC8021789.
- North, B. J., Rosenberg, M. A., Jeganathan, K. B., Hafner, A. V., Michan, S., Dai, J., … & van Deursen, J. M. (2014). SIRT2 induces the checkpoint kinase BubR1 to increase lifespan. The EMBO journal, e201386907.
- Cantó C. Menzies K.J. Auwerx J. NAD(+) metabolism and the control of energy homeostasis: a balancing act between mitochondria and the nucleus. Cell Metab. 2015 Jul 7;22(1):31-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.05.023. Epub 2015 Jun 25. PMID: 26118927; PMCID: PMC4487780.
- Irie, J., Inagaki, E., Fujita, M., Nakaya, H., Mitsuishi, M., Yamaguchi, S., … & Okano, H. (2019). Effect of oral administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide on clinical parameters and nicotinamide metabolite levels in healthy Japanese men. Endocrine journal, EJ19-0313.
- Mihoko Yoshino, Jun Yoshino, Brandon D. Kayser, Gary Patti, Michael P. Franczyk, Kathryn F. Mills, Miriam Sindelar, Terri Pietka, Bruce W. Patterson, Shin-Ichiro Imai, Samuel Klein. Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women. Science, 2021; eabe9985 DOI: 10.1126/science.abe9985
- Liao B, Zhao Y, Wang D, Zhang X, Hao X, Hu M. Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation enhances aerobic capacity in amateur runners: a randomized, double-blind study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021 Jul 8;18(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12970-021-00442-4. PMID: 34238308; PMCID: PMC8265078.
- Stefano Tarantini, Marta Noa Valcarcel-Ares, Peter Toth, Andriy Yabluchanskiy, Zsuzsanna Tucsek, Tamas Kiss, Peter Hertelendy, Michael Kinter, Praveen Ballabh, Zoltán Süle, Eszter Farkas, Joseph A. Baur, David A. Sinclair, Anna Csiszar, Zoltan Ungvari, “Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation rescues cerebromicrovascular endothelial function and neurovascular coupling responses and improves cognitive function in aged mice.” Redox Biology, Volume 24, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101192.